Cloud computing is the on-demand deliver of computer system resources such as computing power, storage and networking over the internet to any location.
Cloud deployment model is defined as specific type of cloud environment that is differentiated by the size, ownership and access of cloud services
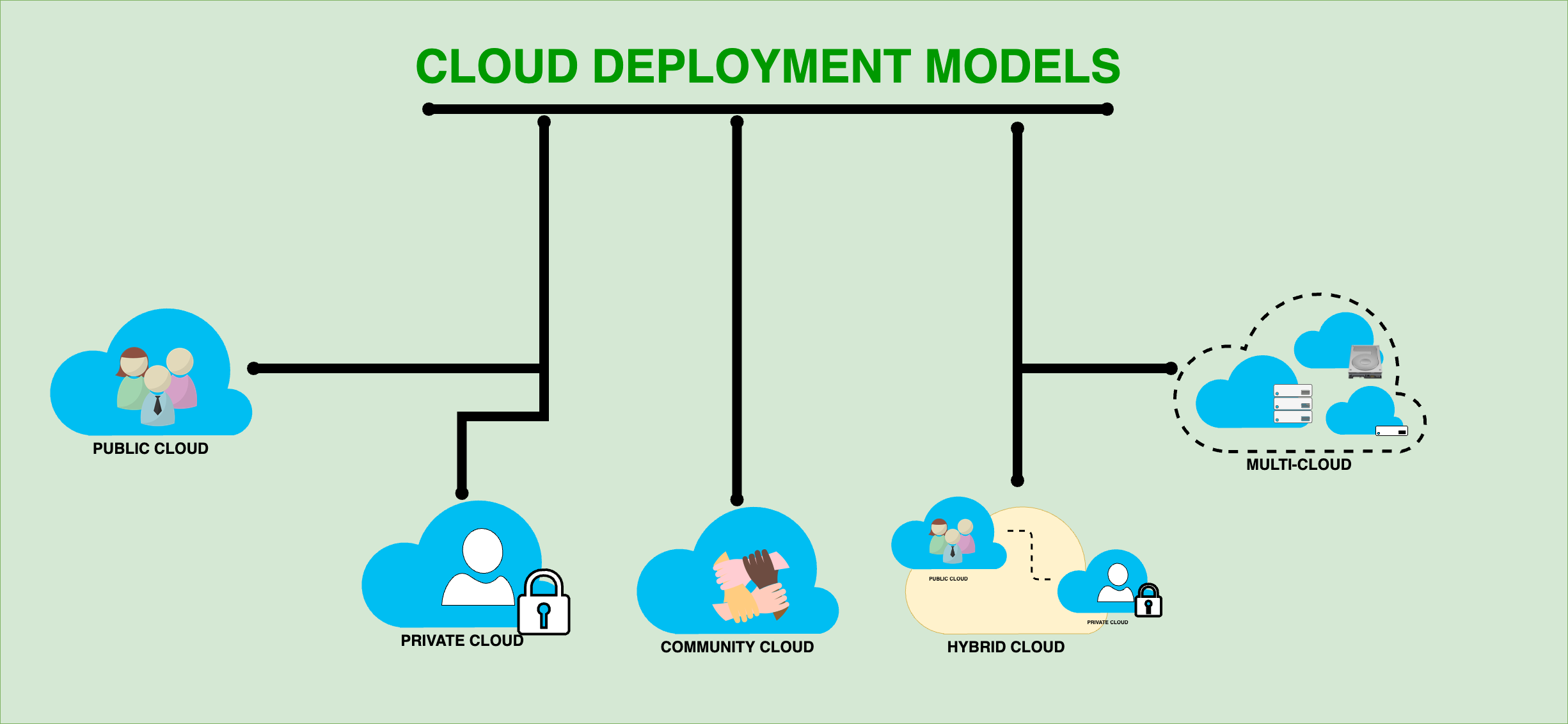
There are four cloud deployment models
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Community Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
- Multi-Cloud
These cloud deployment models are classified based on access, proprietorship and size of cloud infrastructure
Organisation or the person who receives the services from vendor or cloud provider is referred as cloud consumer and the organisation that provides these cloud services is called as cloud provider
Some of the well know cloud providers are Google, Salesforce, Microsoft, Amazon, Zoho and Rackspace
Private Cloud
Private cloud refers to the cloud infrastructure operates for an organization. Private cloud is owned by a specific company or organization, even though it is either self managed or managed by third party. Private cloud servers may exist on premise or off premise. When it comes to private cloud, technically same organisation acts as the both cloud provider and the cloud consumer
- Cloud infrastructure is owned by single organization
- Organization will be both cloud provider and cloud consumer
- Cloud infrastructure can either on-premise or off-premise
- If cloud is on internet, organization members will access typically through VPN
- External access is not permitted
Advantages of Private Cloud
- Complete control – over whole infrastructure
- Information security – Extensive control over organization information
- IT resources like computing power, networking and storage can be customised at will
- Confidentiality of the sensitive data is maintained
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
- Cost Intensive – It takes lot of capital investment for private cloud infrastructure
- High operating overhead – organization solely need to bear operating overhead cost (electricity, space, management etc)
- Acquisition cost – it is required to buy software, hardware, employee training
- Licencing – need to bare complete licensing cost of software required to operate infrastructure
- Human resource – It is required to employee fleet of workers to administrate complete cloud infrastructure
Public Cloud
Public cloud is cloud computing platform that is available to general public owned by cloud(service) provider. Cloud provider manages infrastructure and pool of resources. Public cloud is available to general public or organizations with pay-as-you-go(PAYG)/pay per usage pricing model, IT resources like computing power, storage and database are delivered over internet. It eliminates need of buying and maintaining own hardware and infrastructure.
- Public cloud infrastructure is usually owned by organization who provides cloud as a service called cloud provider
- IT resources like computing power, storage, networking and database are delivered over internet
- Public cloud is publicly accessible to general public which includes individuals & organizations
- IT resources are made available to cloud consumer via one or more cloud delivery models
- IT resources are managed by cloud provider. Type of IT resources that are managed by provider depends on type of cloud delivery model
- Monitoring and analytical tools will be provided by cloud provider to monitor consumption of IT resources
- Cloud provider is responsible for creation and maintenance of provided IT resources
Examples of some public cloud providers are: Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform and IBM Cloud
Public cloud will be available in following cloud delivery models: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS.
Advantages of Public Cloud
- Cost Effective – Company or person need not to worry about huge investment for buying to own computing resources with pay-as-you-go pricing model
- Software Updates – Cloud provider will take of updating necessary of underlying software used for provider managed components
- Bleeding Edge Technology – Using cloud service gives you access to bleeding edge technology
- Elasticity – It is possible to grow or shrink IT resources on demand
- Global Infrastructure – Using established cloud computing services will give access to geographical infrastructure
- Security and Firewall – Security constructs and firewall of cloud provider acts as first life of defense against attacks
- Scalability – Public cloud technologies are endlessly scalable with no constraint of cost of capital investment
- High availability – Cloud provider ensures the 99.999% of uptime with service level agreement (SLA)
- Monitoring & Analytics – Extensive monitoring and auditing capabilities. Example: AWS Cloud Watch
- Ubiquitous Access – Cloud services are accessible from any where using any device, technology or interface
Disadvantages of Public cloud
- Deprived of information – User are not aware of where information is stored if anybody has access
- Technical Support – if not attended, technical support will be devastating in mission critical times
- Less control – Less control over underlying infrastructure or IT resources managed by cloud provider
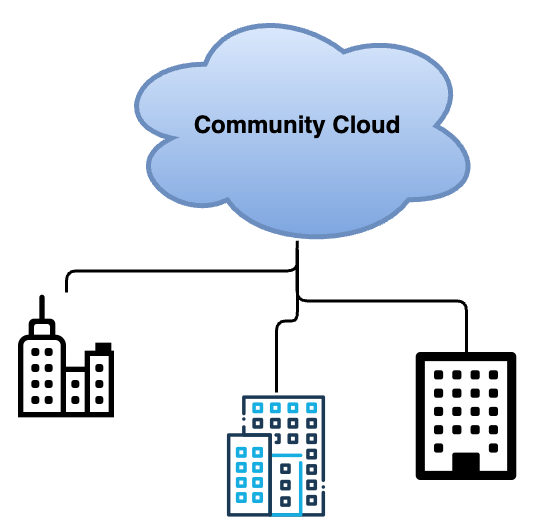
Community Cloud
Community cloud is very similar to public cloud but access is limited among community of different organizations that share common goals. This type of cloud may exist on premise or off premise, owned by either community of cloud consumer or third party. It is not necessary that, all members in the community share same level access control over IT resources of cloud, different members may posses limited of no access to some IT resources.
- Sames as public cloud but access is limited to community of cloud consumers
- Responsibilities are shared among community members
- Community members can be either individuals or organizations
- Community members share the responsibilities of defining and improving cloud
Examples of community clouds include: Cloud shared among different departments of government organizations
Advantages of Community Cloud
- Data Privacy and reliability
- Secured – Access is limited by community of cloud consumers protected by secured network
- Collaboration – It is effective to collaborate with shared community members
- Data Sharing – Data is protected from outside and sharing of data with community members is effective
Disadvantages of Community Cloud
- Costlier than public cloud
- Deployments and provisioning of IT resources may be slower because of shared responsibilities in community
- It is not widely used
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud is a composition of two or more cloud deployment models private, pubic or community. For example the cloud consumer may choose to use private cloud to process the sensitive data or store it and public cloud of computing resource to save operating cost of infrastructure.
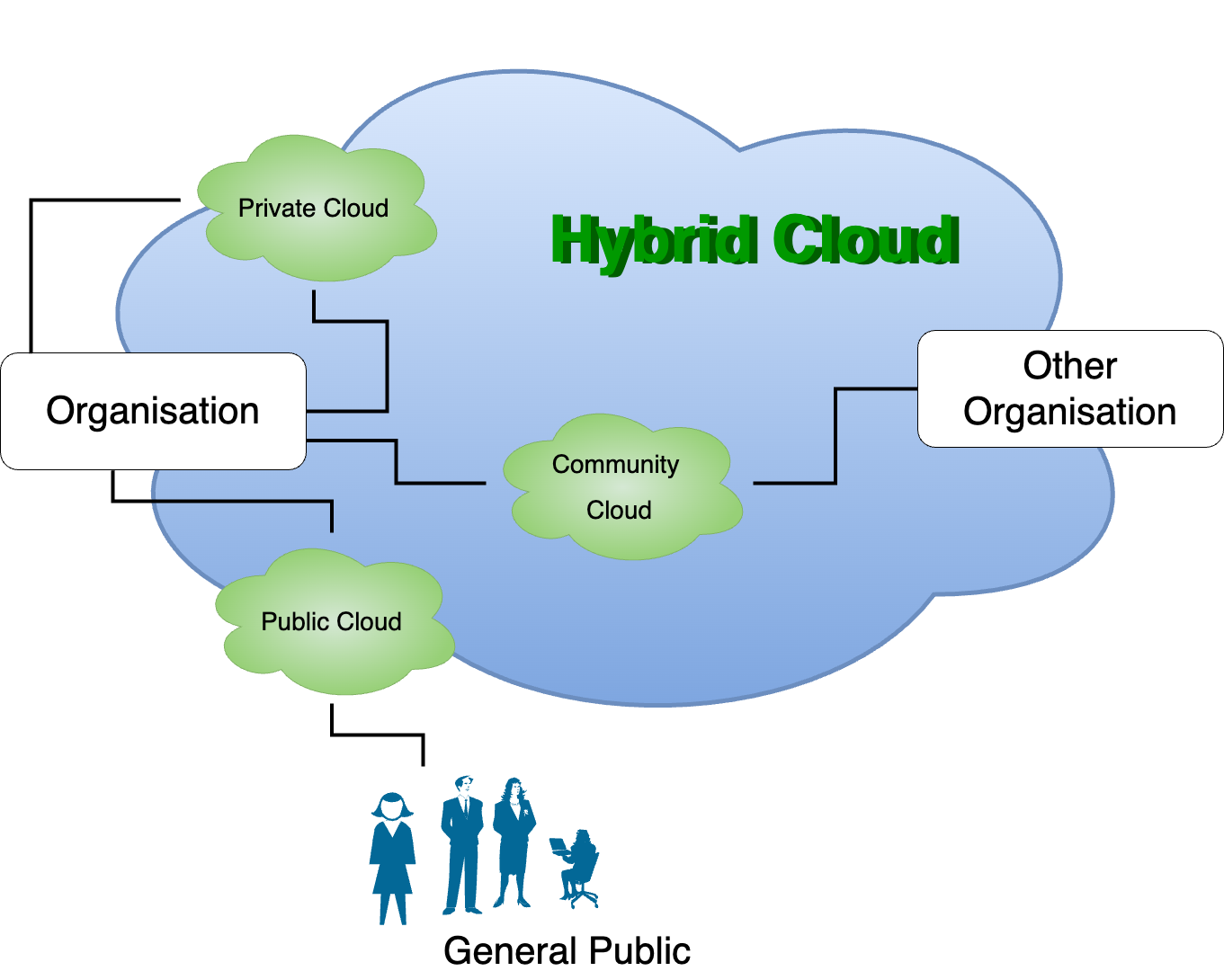
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Improved security compared to public cloud
- Relatively cheaper than whole blown private cloud
- Flexible
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Complex
- Reliable connectivity between cloud infrastructures is required
Multi Cloud
Multi cloud is defined as use of multiple cloud providers to server different needs such as computing, storage and networking in the single heterogenous architecture to benefit the cloud infrastructure.
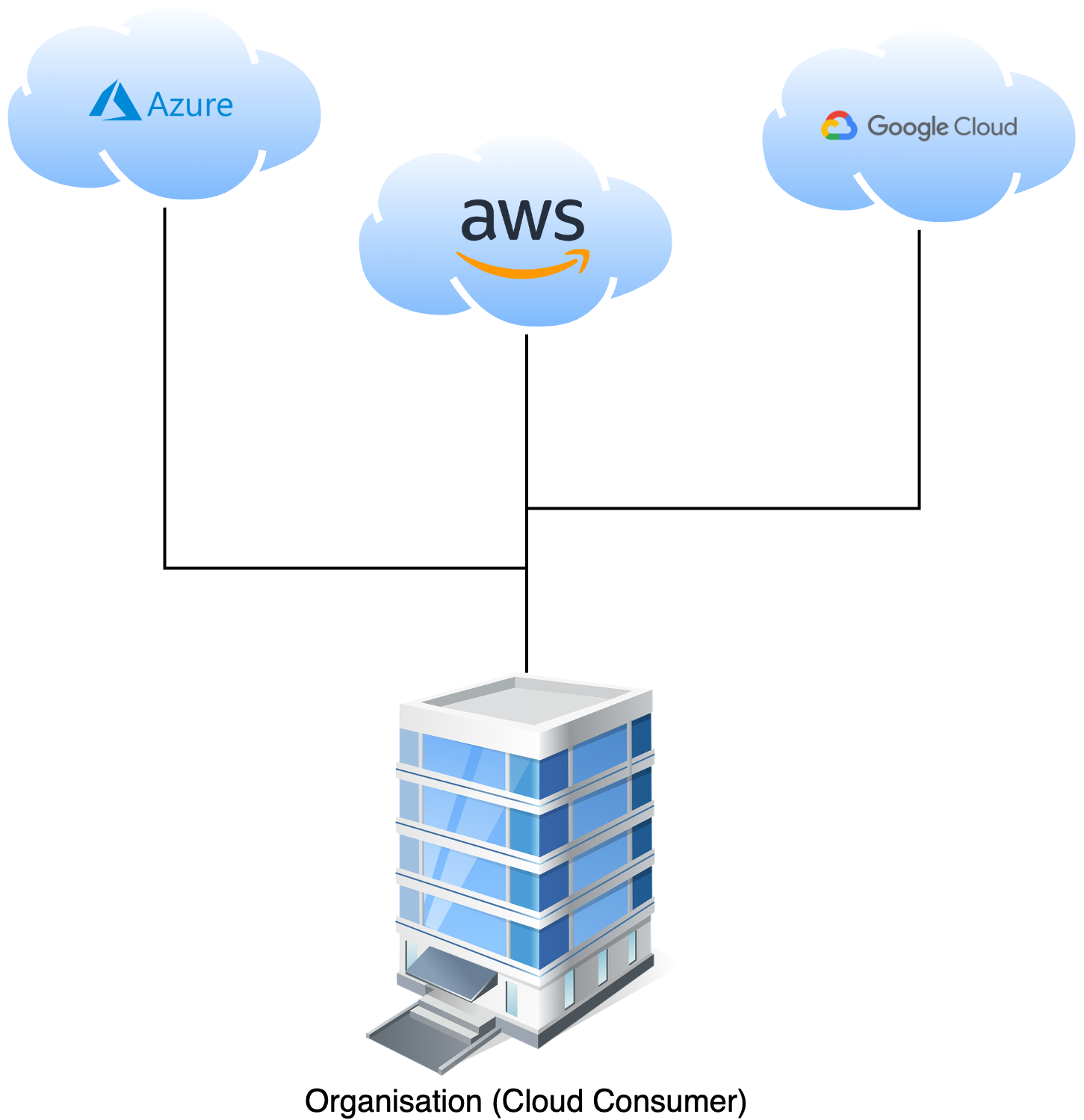
As it is shown in the above figure, one organisation can make use of different public cloud service providers to service it’s business needs. For example: Using IBM IoT platform for IOT technologies, and Dropbox for storage and cloudfront for CDN
Advantages of Multi Cloud
- Improved security compared to public cloud
- No risk of lock in
- Flexible
Disadvantages of Multi Cloud
- Complex
- Reliable connectivity between different cloud providers is required
- Interoperability between cloud providers




Leave a Reply