The command icacls can be used to display or modify discretionary access control list (DACLs).
Syntax of command icacls
icacls [/grant[:r] :[…]] [/deny :[…]] [/remove[:g|:d]] […]] [/t] [/c] [/l] [/q] [/setintegritylevel :[…]] icacls [/substitute […]] [/restore [/c] [/l] [/q]]
Display permissions of a give file
icacls <path to file>When you are accessing or modifying, if permissions are not in place you will get the error saying:
Windows cannot access the specified device,path, or file. You may not have the appropriate permissions to access the item.
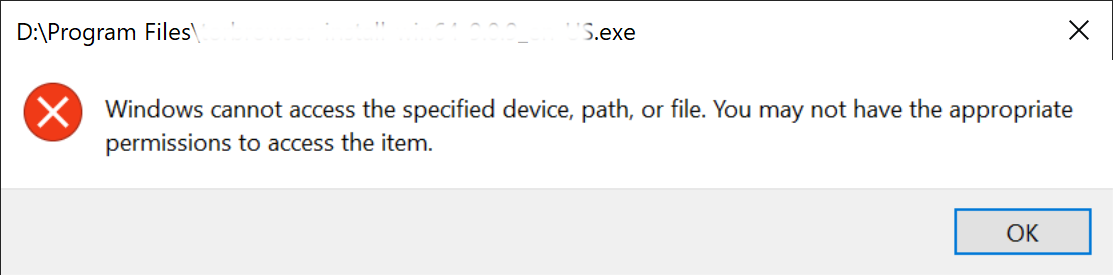
Apparently, if you are not administrator you might not have permissions proper permissions to open that corresponding file. But, there are other reasons that could this permissions problem
This permissions problem could arise
- If you download file using command line using wget or similar software
- Created file(s) using cygwin
With these corrupted permissions, GUI may not respond well if you go properties of file/folder. All permissions can be reset using the command “icacls” as described below
Reset permissions for a given file
icacls <path to file> /reset
Example: icacls .\filetoreset.txt /reset
Reset permissions for a given folder
icacls <path to folder> /reset
Reset permissions for a folder including it’s files and folders
icacls <path to folder> /reset /t /c /l
To give the specific group name users full control to specified folder
icacls "D:\Folder" /grant Users:FIts sister PowerShell command “Get-Acl” can also be used to display all permissions associated with given file
Here is the syntax for the command icacls
ICACLS name /save aclfile [/T] [/C] [/L] [/Q]
stores the DACLs for the files and folders that match the name
into aclfile for later use with /restore. Note that SACLs,
owner, or integrity labels are not saved.
ICACLS directory [/substitute SidOld SidNew [...]] /restore aclfile
[/C] [/L] [/Q]
applies the stored DACLs to files in directory.
ICACLS name /setowner user [/T] [/C] [/L] [/Q]
changes the owner of all matching names. This option does not
force a change of ownership; use the takeown.exe utility for
that purpose.
ICACLS name /findsid Sid [/T] [/C] [/L] [/Q]
finds all matching names that contain an ACL
explicitly mentioning Sid.
ICACLS name /verify [/T] [/C] [/L] [/Q]
finds all files whose ACL is not in canonical form or whose
lengths are inconsistent with ACE counts.
ICACLS name /reset [/T] [/C] [/L] [/Q]
replaces ACLs with default inherited ACLs for all matching files.
ICACLS name [/grant[:r] Sid:perm[...]]
[/deny Sid:perm [...]]
[/remove[:g|:d]] Sid[...]] [/T] [/C] [/L] [/Q]
[/setintegritylevel Level:policy[...]]
/grant[:r] Sid:perm grants the specified user access rights. With :r,
the permissions replace any previously granted explicit permissions.
Without :r, the permissions are added to any previously granted
explicit permissions.
/deny Sid:perm explicitly denies the specified user access rights.
An explicit deny ACE is added for the stated permissions and
the same permissions in any explicit grant are removed.
/remove[:[g|d]] Sid removes all occurrences of Sid in the ACL. With
:g, it removes all occurrences of granted rights to that Sid. With
:d, it removes all occurrences of denied rights to that Sid.
/setintegritylevel [(CI)(OI)]Level explicitly adds an integrity
ACE to all matching files. The level is to be specified as one
of:
L[ow]
M[edium]
H[igh]
Inheritance options for the integrity ACE may precede the level
and are applied only to directories.
/inheritance:e|d|r
e - enables inheritance
d - disables inheritance and copy the ACEs
r - remove all inherited ACEs
Note:
Sids may be in either numerical or friendly name form. If a numerical
form is given, affix a * to the start of the SID.
/T indicates that this operation is performed on all matching
files/directories below the directories specified in the name.
/C indicates that this operation will continue on all file errors.
Error messages will still be displayed.
/L indicates that this operation is performed on a symbolic link
itself versus its target.
/Q indicates that icacls should suppress success messages.
ICACLS preserves the canonical ordering of ACE entries:
Explicit denials
Explicit grants
Inherited denials
Inherited grants
perm is a permission mask and can be specified in one of two forms:
a sequence of simple rights:
N - no access
F - full access
M - modify access
RX - read and execute access
R - read-only access
W - write-only access
D - delete access
a comma-separated list in parentheses of specific rights:
DE - delete
RC - read control
WDAC - write DAC
WO - write owner
S - synchronize
AS - access system security
MA - maximum allowed
GR - generic read
GW - generic write
GE - generic execute
GA - generic all
RD - read data/list directory
WD - write data/add file
AD - append data/add subdirectory
REA - read extended attributes
WEA - write extended attributes
X - execute/traverse
DC - delete child
RA - read attributes
WA - write attributes
inheritance rights may precede either form and are applied
only to directories:
(OI) - object inherit
(CI) - container inherit
(IO) - inherit only
(NP) - don't propagate inherit
(I) - permission inherited from parent container
Examples:
icacls c:\windows\* /save AclFile /T
- Will save the ACLs for all files under c:\windows
and its subdirectories to AclFile.
icacls c:\windows\ /restore AclFile
- Will restore the Acls for every file within
AclFile that exists in c:\windows and its subdirectories.
icacls file /grant Administrator:(D,WDAC)
- Will grant the user Administrator Delete and Write DAC
permissions to file.
icacls file /grant *S-1-1-0:(D,WDAC)
- Will grant the user defined by sid S-1-1-0 Delete and
Write DAC permissions to file.



Leave a Reply