There are lot of command line tools available in Linux to dump files as ASCII, decimal, hexadecimal, octal and binary forms. Often it will be helpful when you want to study internals of any file structure or debugging/troubleshooting network systems. This article will introduce you to various available command line tools on Linux to dump files in different formats like octal, hexadecimal and binary. Major hexdump tools available on Linux include hexdump, od and xxd.
Hexdump command line tools are also play vital role in computer forensics to investigate content of binary files.
hexdump Command
Command line tool hexdump is available at disposal on most Linux disbributions. This tool is available on most Linux distributions by default. Command hd is an alias for hexdump
hexdump command usage
hexdump [-bcCdovx] [-e fmt] [-f fmt_file] [-n length]
[-s skip] [file ...]
hd [-bcdovx] [-e fmt] [-f fmt_file] [-n length]
[-s skip] [file ...]To quickly hexdump data of a give file. hexdump <path to file>
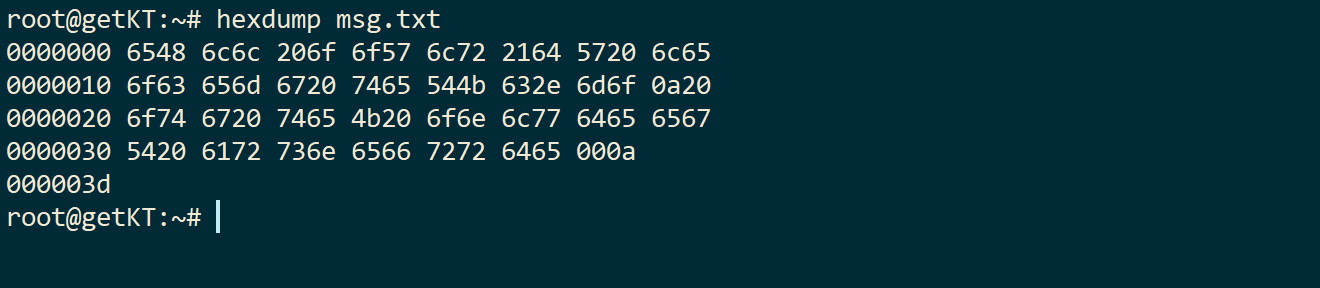
hedump msg.txt
xxd Command
The command xxd provides lot more flexibility compared to hexdump. This command xxd can be used to dump content as binary, octal and hexadecimal strings.
Usage of comand xxd
Usage:
xxd [options] [infile [outfile]]
or
xxd -r [-s [-]offset] [-c cols] [-ps] [infile [outfile]]
Options:
-a toggle autoskip: A single '*' replaces nul-lines. Default off.
-b binary digit dump (incompatible with -ps,-i,-r). Default hex.
-c cols format octets per line. Default 16 (-i: 12, -ps: 30).
-E show characters in EBCDIC. Default ASCII.
-e little-endian dump (incompatible with -ps,-i,-r).
-g number of octets per group in normal output. Default 2 (-e: 4).
-h print this summary.
-i output in C include file style.
-l len stop after octets.
-o off add to the displayed file position.
-ps output in postscript plain hexdump style.
-r reverse operation: convert (or patch) hexdump into binary.
-r -s off revert with added to file positions found in hexdump.
-s [+][-]seek start at bytes abs. (or +: rel.) infile offset.
-u use upper case hex letters.
-v show version: "xxd V1.10 27oct98 by Juergen Weigert".
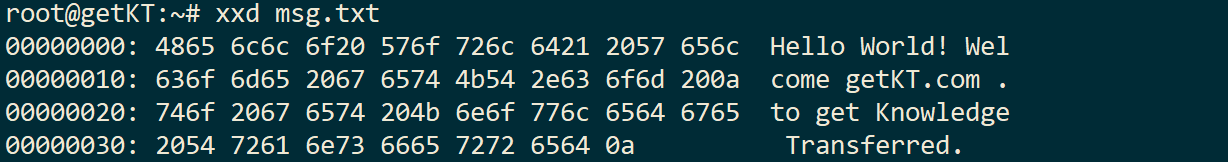
Quickly dump content of file in hex format, run xxd <path to file>
xxd msg.txt
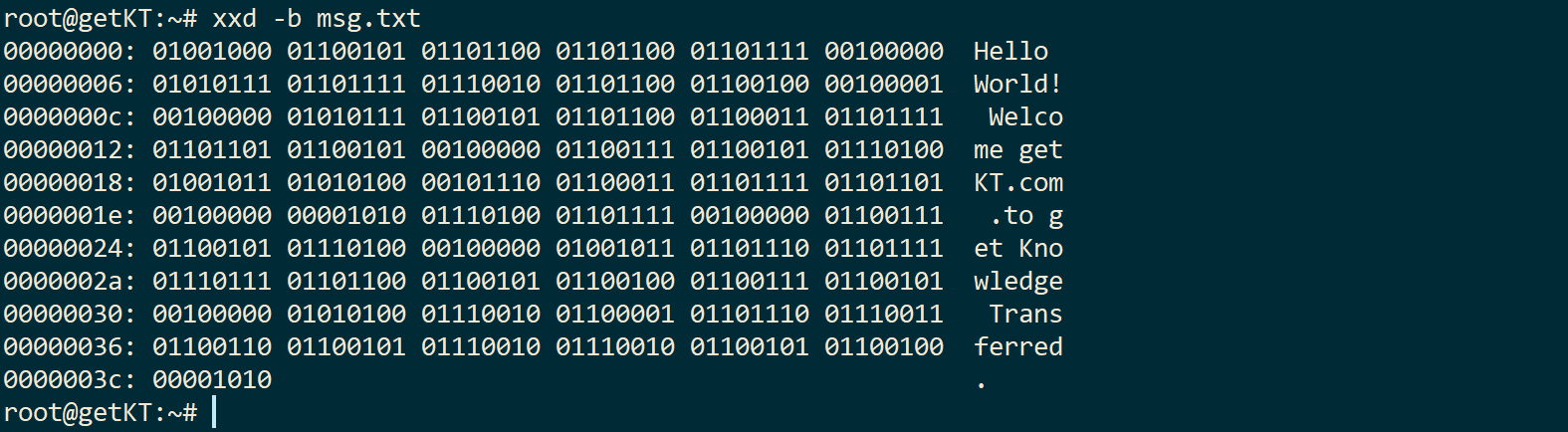
Dump content of file in binary (digits bits 1 or 0).
xxd -b msg.txt
The command xxd is quite useful, see full potential of this command at #TBA
od Command
The command od can also be used to dump files in binary, hex and octal formats. This command od can also be used to swap byte order. Where od is an acronym for “octal dump”
Syntax of command od
od [OPTION]... [FILE]...
od [-abcdfilosx]... [FILE] [[+]OFFSET[.][b]]
od --traditional [OPTION]... [FILE] [[+]OFFSET[.][b] [+][LABEL][.][b]]Hexcurse
The command hexcurse is more of a ncurses-based hex editor. It will not only display hexadecimal strings and actual message in split view but also allow you to edit hexadecimal strings
Install on Debian Based System (Ubuntu)
apt install -y hexcurse
Syntax of command hexcurse
hexcurse [ -? | -help ] [ -a ] [ -r rnum ] [ -o outputfile ] [ [ -i ] inputfile ]Command usage
hexcurse [-?|help] [-a] [-r rnum] [-o outputfile] [[-i] infile]
-a Output addresses in decimal format initially
-e Output characters in EBCDIC format rather than ASCII
-r rnum Resize the display to "rnum" bytes wide
-o outfile Write output to outfile by default
-? | -help Display usage and version of hexcurse program
[-i] infile Read from data from infile (-i required if not last argument)Keyboard shortctus
│ CTRL+? Help - help screen
│ CTRL+S Save - saves the current file open
│ CTRL+O Open - opens a new file
│ CTRL+G Goto - goto a specified address
│ CTRL+F Find - search for a hex/ascii value
│ CTRL+A HexAdres - toggle between hex/decimal address
│ TAB Hex Edit - toggle between hex/ASCII windows
│ CTRL+Q Quit - exit out of the program
│ CTRL+U Page up - scrolls one screen up
│ CTRL+D Page down- scrolls one screen down
│ CTRL+Z Undo - reverts last modification
│ CTRL+T Home - returns to the top of the file
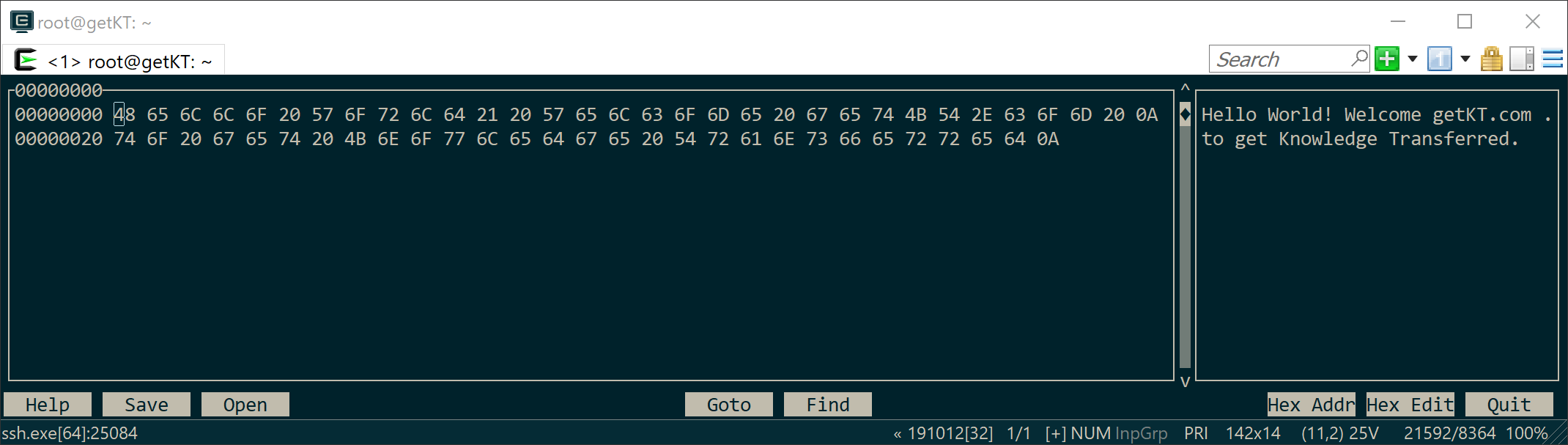
│ CTRL+B End - jumps to the bottom of the fileTo open selected file in hexcurse: hexcurse <path to file>
hexcurse msg.txt
Hexyl
Wow! this is just an amazing tool. This tools visualizes raw text or binary data in the form hexadecimal and ASCII formats in different categories in colored output. This can be quite useful to understand, learn and troubleshoot internals of different binary file formats
To Install on Debian Based Systems (Ubuntu)
apt install -y hexyl
Syntax of hexyl
hexyl [OPTIONS] [file]
hexdump using command hexyl
hexyl msg.txt

Vim Editor
Text editor “vim” can also be used to view and edit files in the form of hexadecimal or binary. Vim allows other Linux commands to be executed inside in command mode like ls, mkdir and rm. Using this feature another command like xxd or hexdump is used to display actual data in either binary or hexadecimal format.
Display text as 16-bit hexdecimal strings
:%!xxd
Following image shows reading of hexdump of a file into current buffer
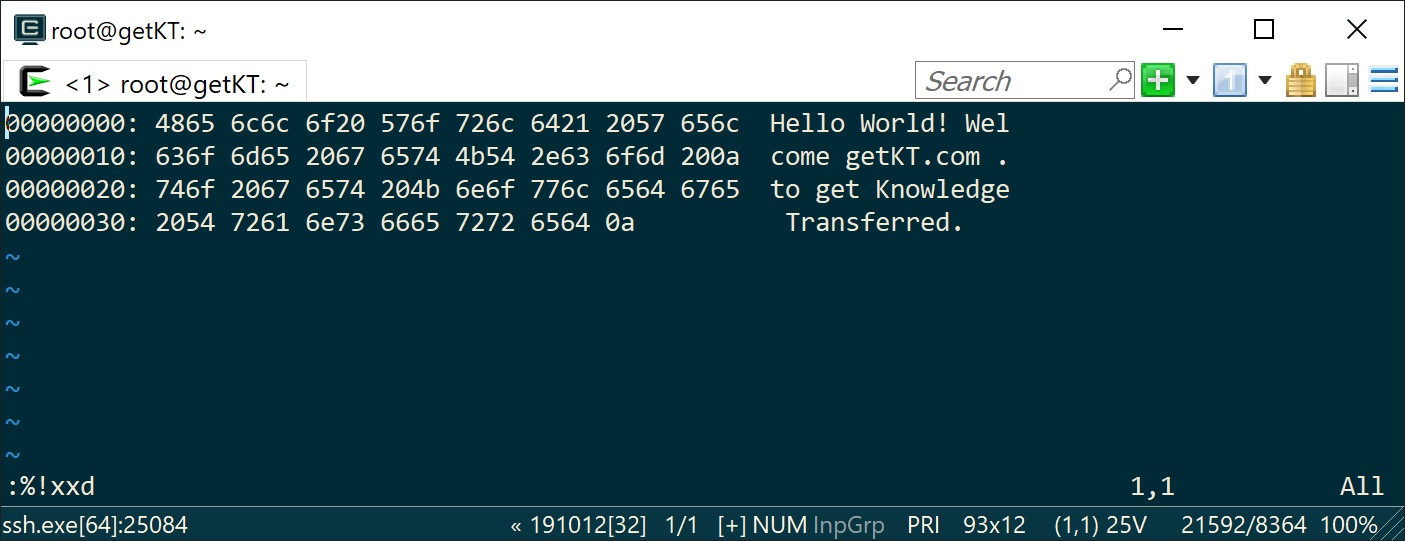
You may edit hex bytes then convert back to normal. Use following command to turn content back to normal text (binary)
:%!xxd -r
To display binary strings (ones and zeros)
:%!xxd -b
To return back to normal, as shown earlier use :%xxd -r
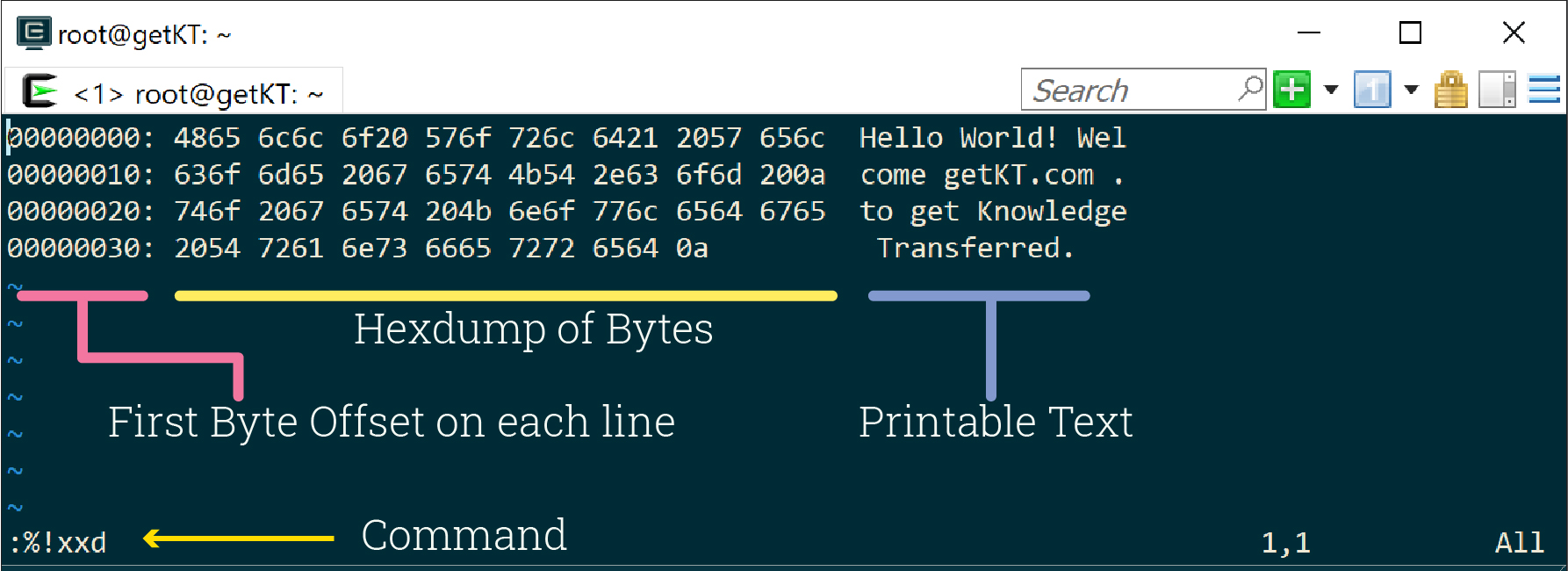
As you use the command xxd to display content in binary, content will be displayed in different columns. Following images identifies the different components or areas in the output of :%!xxd command used inside vim. Vim text editor will not only allow you to dump files in different formats like binary, octal and hexadecimal using different hexdump commands but also would allow to edit files in those formats.
Emacs Editor
Emacs is great text editor. Lot of Linux distributions ship with Emacs. Emacs has special mode for editing binary files called “Hexl mode”. To switch to Hexl mode, use “M-x hexl-mode” to display current buffer or opened file into hex. This mode is especially helpful to edit binary files. When you switch to Hexl mode file is displayed in hex and will be converted back to binary when you save automatically
Switch to Hexl Mode
M-x hexl-mode
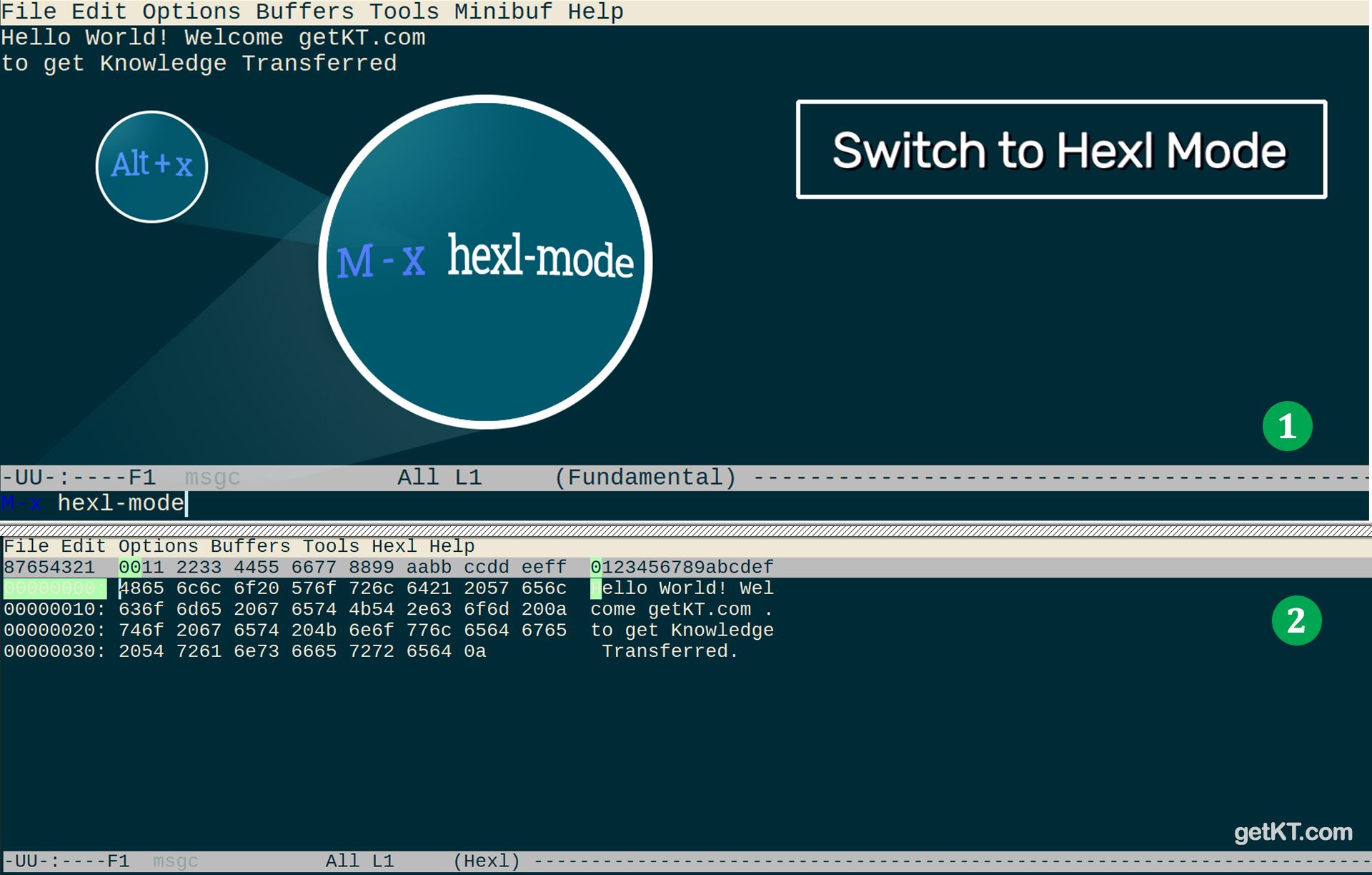
As shown in above figure, once switched to Hexl mode. Current buffer will be displayed in hex format. Data is displayed in 3 columns. First column contains the offset of first byte in a line, second column contains hexadecimal representation of binary data and third column shows content of file as printable characters (ASCII)
Command statements in Emacs begin with either Ctrl or Meta keys
M meas meta key which is usually the Alt
C stands for Ctrl
To initiate a command “M-x” type Alt + x
For suppose command to exit Emacs is “C-x C-c” which means type Ctrl + x followed by Ctrl + c
Following commands will help to work with and navigate through content in Hexl mode
| C-M-d | Insert a byte by taking input in decimal |
| C-M-o | Insert a byte by taking input in octal |
| C-M-x | Insert a byte by taking input in hex |
| C-M-b | Move Backward Short |
| C-M-f | Move Forward Short |
| C-M-a | Beginning of 512 byte page |
| C-M-e | End of 512 byte page |
| C-x [ | Move to Beginning of 1K page |
| C-x ] | Move to End of 1K page |
| M-g | Move to an address given in hex |
| M-j | Move to an address given in decimal |
| C-c C-c | Exit Hexl mode to go back to normal mode or previous buffer you had before switching to Hexl mode |




Leave a Reply